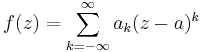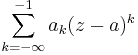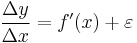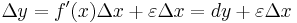Principal part
In mathematics, the principal part has several independent meanings, but usually refers to the negative-power portion of the Laurent series of a function.
Contents |
Laurent series definition
The principal part at 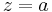 of a function
of a function
is the portion of the Laurent series consisting of terms with negative degree. That is,
is the principal part of  at
at 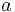 .
. 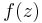 has an essential singularity at
has an essential singularity at 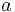 , if and only if the principal part is an infinite sum.
, if and only if the principal part is an infinite sum.
Other definitions
Calculus
Consider the difference between the function differential and the actual increment:
The differential dy is sometimes called the principal (linear) part of the function increment Δy.
Distribution theory
The term principal part is also used for certain kinds of distributions having a singular support at a single point.